SSC and PAH
SSC and PAH

What is PAH?
A subtype of pulmonary hypertension (PH)
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare, progressive disease characterised by elevated pulmonary arterial pressure and vascular resistance that eventually leads to right ventricular failure and death[1]
Early identification and intervention are key to changing the course of the disease[2]
PAH is a severe and often fatal complication of CTD:[3]
- It is most commonly seen in SSc, accounting for 75% of CTD-PAH cases[4]
- Approximately 1 in 10 patients with SSc are estimated to have PAH[5]
PAH is a leading cause of death in patients with SSc, accounting for >50% of deaths in SSc-PAH patients[6]
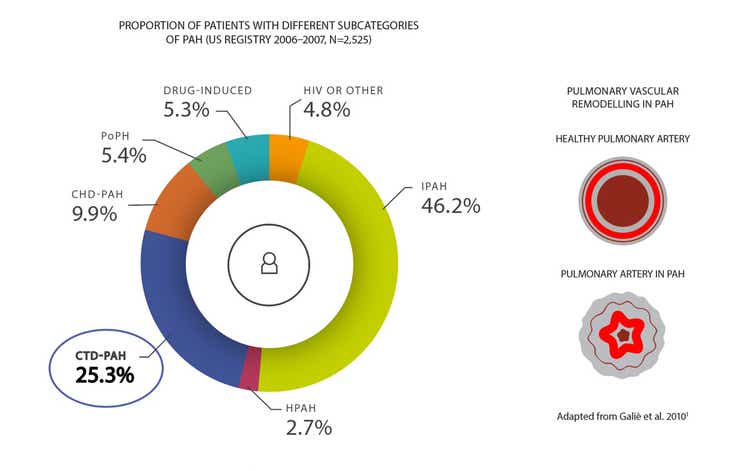
Adapted from Badesch et al. 2010[7]
Early identification of PAH in patients with SSc is critical
Early recognition of PAH in SSc is difficult; symptoms at disease onset are mild and the complex nature of SSc makes interpretation of fatigue and breathlessness challenging[8]
However, early evaluation can lead to prompt referral and confirmation – and improved patient outcomes
When evaluating a patient with SSc, it is vital to look at the complete picture, including:
1. Patient history
- Increasing breathlessness, reduced exercise tolerance, chest pain, ankle swelling and presyncopal symptoms could indicate the presence of PAH in your SSc patients[9]
- These symptoms should prompt immediate consideration of PAH in your SSc patient[10]
2. Clinical examination
- Look for features of right ventricular (RV) dysfunction[10]
- Examine for an RV heave and raised jugular venous pressure (JVP)[10][11]
3. Non-invasive screening tests
- Right heart echocardiography[12]
- DLCO[12]
- Circulating N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP)[12]
Screening model helps the path to referral
Screening SSc patients for PAH can lead to early diagnosis and improvements in long-term outcomes compared with diagnosis during routine care[13]
It is therefore recommended that all asymptomatic patients with SSc are screened for PAH annually and referred for right heart catheterisation (RHC) if PAH is suspected[12]
2015 ESC/ERS guidelines - screening strategy
Referral for RHC can be recommended, depending on the echocardiographic probability of PAH
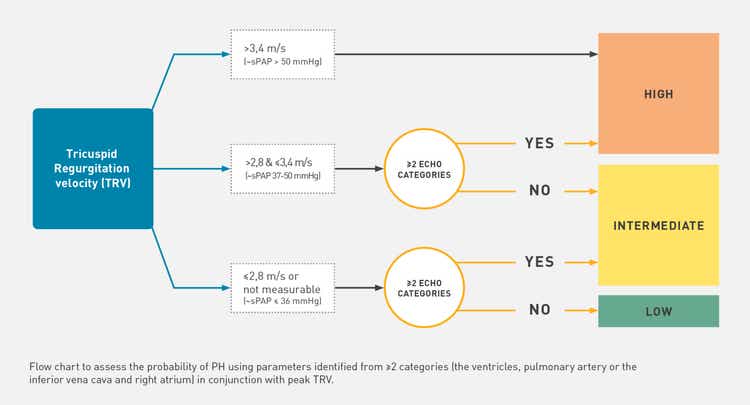
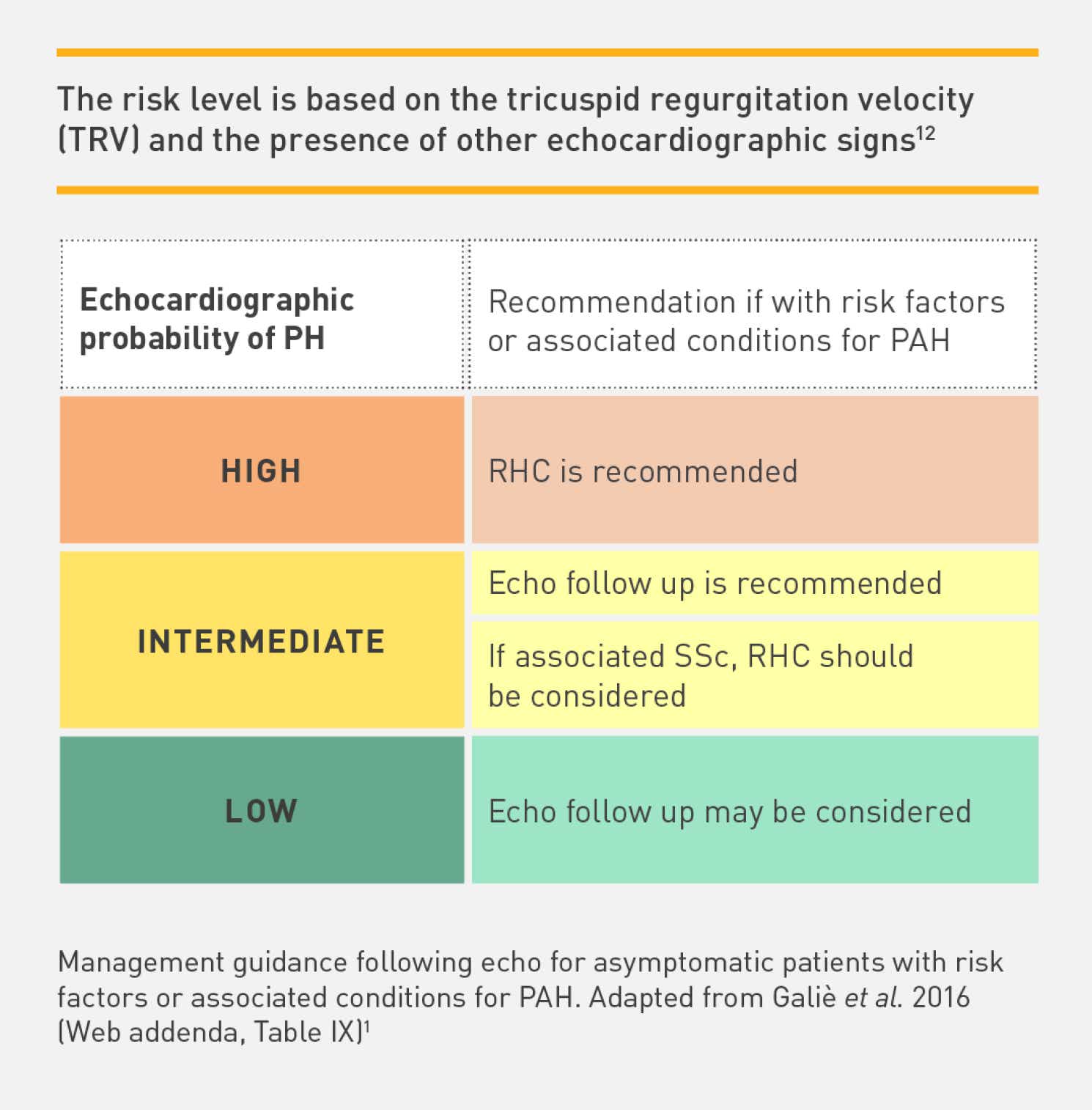
DLCO: in-depth clinical follow-up is necessary for patients with a moderate to severe decrease.[12]
NT-proBNP (ng/l):[12]

Early referral of SSc-PAH patients is critical
PAH remains a major cause of mortality in SSc[10]
Unlike idiopathic PAH, clinicians have the opportunity to actively screen for SSc-PAH and refer to a specialist PH centre to confirm diagnosis with RHC[15]
Screening for PAH in patients with SSc can lead to an increase of 47% in survival after 8 years vs those detected during routine clinical practice[15]
Impact of screening on survival in patients with SSc-PAH
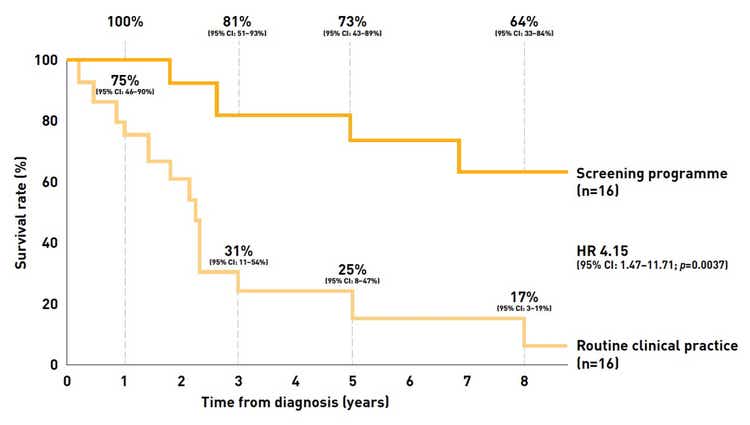
Adapted from Humbert et al. 2011[15]
Early treatment of PAH can delay disease progression and improve long-term outcomes for your patients with SSc-PAH[16][17][18][19]
Find out how your patients could benefit from our current therapies in PAH.
Contact
Want to know more? Contact our medical team!

Medical Science Liaison Netherlands
+31 6 25511970
igroot@its.jnj.com
Do you have a question for us or did you not find what you were looking for? Let us know and one of our Janssen-specialists will contact you as soon as possible.
Discover Janssen's portfolio and the matching SmPC's.
On this page you will find interactive 3D animations of the human anatomy and various syndromes. This allows you to zoom in on the anatomy, tissue structures, disease mechanisms and the course of the disease.
Abbreviations
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase;CHD, congenital heart disease; CI, confidence interval; CTD, connective tissue disease; ERA, endothelin receptor antagonist; ERS, European Respiratory Society; ESC, European Society of Cardiology; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HPAH, heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension; HR, hazard ratio; IPAH, idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension; LFT, liver function test; PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension; PH, pulmonary hypertension; PoPH, portopulmonary hypertension; RHC, right heart catheterisation; SSc, systemic sclerosis; TRV, tricuspid regurgitation velocity; ULN, upper limit of normal; 6MWD, six-minute walk distance